Dermatitis is a common skin disease caused by a fungus that affects people of all ages. It typically causes irritation, itching and inflammation of the skin. Some forms of dermatitis are also known as stasis dermatitis and chronic dermatitis
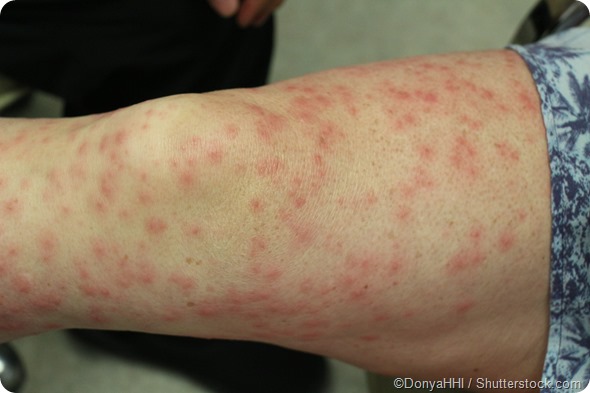
Contact dermatitis causes your skin to be itchy, blistery, dry and red. Light skin may become red, pink or gray, and dark skin may become dark brown, blue or purple. The reaction usually happens within a few days or weeks of contact with an irritant. Other types of dermatitis include atopic dermatitis, which affect children; seborrheic dermatitis, which affect the face, neck and armpits; rosacea, which affect the cheeks, forehead and eyes; and psoriasis, which affects the scalp and body areas. Dermatitis may also cause skin irritation, redness and scaling, sometimes called hives, itching or flaking.
A variety of factors can trigger contact dermatitis, including stress, hormonal changes, illness, medications and environmental irritants such as pollution, heat and humidity. In children, irritants include dust mites, flea bites and eczema. They may also develop dermatitis from being exposed to allergens. The most common allergens are household dust mites, mold spores and pet dander.
As we age, our immune system's ability to fight infections decreases. Some of the symptoms of aging may include rashes, itchiness, redness, itching and swelling. Some forms of dermatitis are often confused with wrinkles. For example, atopic dermatitis (atopic eczema) is very similar to rosacea, but is much less noticeable and less uncomfortable. People with chronic skin diseases such as psoriasis and herpes also have skin redness and swelling, as well as blistering and itching.
Many people believe that contact dermatitis results from a person's exposure to something or another that triggers an allergic reaction. A common example is a common insect bite or rash. However, it is important to note that not all allergies can be attributed to contact dermatitis. Many forms of eczema, such as contact dermatitis or atopic eczema, are actually allergic to allergensins.
It has been found that there are a number of underlying causes for dermatitis. These causes may include allergies to foods, skin irritants, stress and skin care products. It is not known what causes dermatitis in everyone, although some people seem to be genetically predisposed to dermatitis.
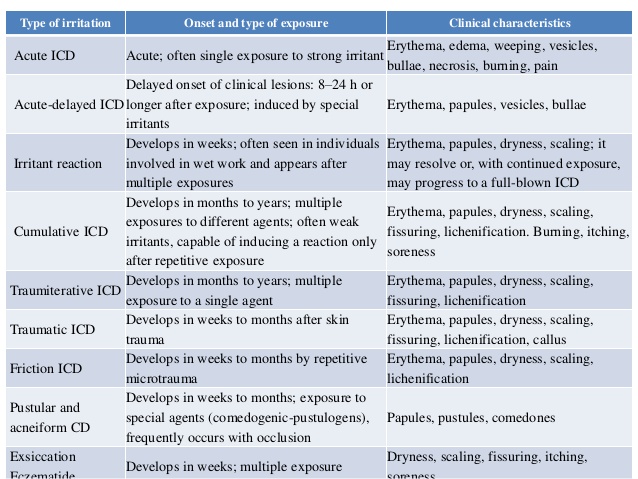
Eczema, often referred to as dermatitis is a very common type of skin condition. The first step for treating it is to identify the allergen causing the problem. The second step is to eliminate the allergen from the sufferer's diet or skin care product regimen, if present. The third step is to keep the allergy away. The fourth step is to prevent the allergen from recurring, usually by keeping the affected area clean and dry, and applying creams or lotions, sometimes containing cortisone or other prescribed medicines, to the affected area. In severe cases, doctors may recommend surgery.
Atopic dermatitis and seborrhea can also be treated with a combination of topical or oral medications, sometimes in combination with prescription topical medications. Sometimes, laser therapy may be used to help eliminate the condition. In severe cases, medical intervention may be needed. This type of treatment is usually recommended only in the most severe cases.
Eczema affects the skin in many different ways, depending on the type of eczema and where it is located. It can range from extremely itchy too painful to being itchy or even painful, then being extremely painful for extended periods of time. It may be a constant itch, but it may be accompanied by inflammation, redness, itchiness and sometimes swelling.
There may be no specific cause for the skin condition, although it is thought that there are certain types of eczema that can occur together. For example, atopic eczema can occur due to allergies to foods, and both atopic dermatitis and seborrhea can occur due to a buildup of dead skin cells on the scalp. While some of these conditions are more common than others, many are completely unrelated and cannot be tied to one another. Some individuals with a hereditary tendency to atopic dermatitis or seborrhea may have a sensitivity to various substances such as: detergents or perfumes. Others may have a genetic predisposition to eczema, which may result in an allergic response to certain substances in foods.
If left untreated, some types of eczema can lead to serious problems. It can lead to premature baldness or even skin cancer.