A urine test to measure the amount of a certain blood protein (microalbumin) in the urine is often referred to as a serum albumin test.
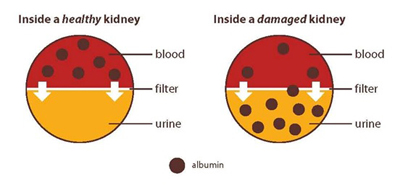
Microalbuminuria is an abnormal increase in the amount of microalbumenal protein in urine, sometimes referred to as albuminuria. A normal value for microalbumenal protein in urine is less than two grams/day. A serum albumin level that is more than two g/L may indicate kidney damage, kidney cancer and other diseases related to kidney function. The condition is quite common in both children and adults and often only diagnosed when it leads to symptoms or failure of kidney function.
Serum albumin levels can be measured by using a simple enzyme immunoassay or with a specialized serum albumin analyzer. The most commonly used blood testing for albumin is known as albumin electrokinetics.
Serum albumin levels can also be determined by using high-sensitivity urine tests (HSU), such as the urea nitrogen (blood urea nitrogen), creatinine and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) tests.

In addition, serum albumin can be determined by using a simple radioimmunoassay called radioisotope probe of albumin and creatinine, the main substances found in albumin.
Microalbuminuria is usually a result of an impaired kidney function. The kidneys are responsible for removing waste products from the body and maintaining healthy levels of fluid, electrolytes and hormones. When the kidneys are impaired, excess albumin in urine increases and this can lead to a decreased renal function. In these cases, it is difficult to determine whether an individual is suffering from microalbumenal proteinuria or a more serious health condition.
Kidney diseases such as nephrocalcinosis and nephrotic syndrome, which cause increased albuminuria in urine, are both linked to an increased production of albumin by the kidneys. The kidneys have a large collection of proteins called the albuminous, which is found in the kidney tissue and contributes to the production of albumin by the kidney.
Kidney disease, such as nephrotic syndrome, kidney cancer and hepatitis, are all diseases of the kidneys, not related to the albumin.
The albumin and albuminomas are often found together in the same fluid and are often confused for a single condition called albuminuria.
The diagnosis of any disease can depend on many factors including the type of disease, its severity, location, the frequency of symptoms and other medical conditions that may cause or contribute to the condition. Microalbumenia can also occur in patients with normal kidney function but are rarely found in patients with kidney disease or in those who do not have any symptoms. For these reasons, doctors often rely on the results of routine laboratory tests as the basis of the diagnosis.
The best way to avoid getting albuminuria is to eat foods that contain high amounts of protein and to avoid urinating while you are having a meal. Some common sources of protein are dairy products, meats and eggs, so adding one of these foods a couple of hours before you have your next meal can help prevent excessive urination. The consumption of protein-rich foods should not interfere with your daily diet and, if necessary, consult a doctor about changing your diet.